 Many
people don't know the signs of drug addiction and addiction symptoms until
someone in their life admits to being an addict. In many cases, this is too
late to prevent the damage addiction can do to the addict and those around
them. Knowing what addiction symptoms to look for can help identify a problem early
and provide the best chance at successful drug recovery.
Many
people don't know the signs of drug addiction and addiction symptoms until
someone in their life admits to being an addict. In many cases, this is too
late to prevent the damage addiction can do to the addict and those around
them. Knowing what addiction symptoms to look for can help identify a problem early
and provide the best chance at successful drug recovery.
Other times, it is harder to spot the signs of drug addiction.
Repeated alcohol binges, for example, might be one of the signs of drug
addiction but isn't always. Signs of drug addiction have to be considered with
addiction symptoms and other information to indicate whether drug addiction is
an issue.
Here are some other
common symptoms of prescription drug abuse or
addiction:
·
Alterations
in mood
·
Erratic
behavior
·
Confusion
·
Hyperactive,
increased alertness
·
Suicidal
tendencies
·
Excessive
sweating, urination or thirst
·
Nausea
and vomiting
·
Uncontrollable
diarrhea
·
Spastic
shaking
·
Drowsiness,
dizziness and insomnia
· Unpleasant
or painful symptoms when substance is withdrawn
The
basic symptoms of drug addiction include:
·
An inability to stop taking the drug, in spite of multiple
attempts
·
Negative consequences to the drug user and those around them
caused by drug use
·
The drug user continues to take greater amounts of the drug
· Withdrawal symptoms when not using the drug
Just
like illegal drugs, prescription drugs also have numerous side effects and
toxicity from these drugs is common. Like all individuals who abuse illicit
drugs, individuals who abuse prescription drugs also deny that they have a
problem. The majority of these individuals have medical conditions which are
obvious but the prescription drug problem is hidden. The majority of these
individuals may have social, emotional problems, stress, depression, anxiety,
financial woes or familial problems.
A
gradual change in these individuals may give a hint to their problem of
prescription drug abuse. These changes include:
·
a
change in friends
·
declining
interest in health
·
decreased
interest in school
·
isolation
from family and old friends
·
repeated
lies, stealing
·
withdraws
from social activities
Health
Effects
 |
| Health Effects |
·
Side
effects of Opioids (respiratory depression, low BP, nausea, vomiting)
·
Side
effects of Benzodiazepines (sedation, coma, decreased respiration, lethargy,
mental confusion)
·
Side
effects of Stimulants (fever, fast heart rate, increased BP, seizures)
General signs of drug addiction include:
·
Secretive behavior, lying
·
Unexplained expenditures
·
Disciplinary action at work or school
·
Legal problems relating to drug use
·
Mood swings, depression, anger, aggression, violence
·
Forgetfulness
·
Frequent illness
·
Presence of drug paraphernalia
·
Using room deodorizers and lozenges to cover drug smells in the
air and the breath
·
Choosing drug use over all else, giving up previously enjoyed
activities
·
Engaging in risky behaviors, contracting a sexually-transmitted
illness
·
Being around other drug users or trying to get others to use
drugs
Drug
addiction symptoms, too, are individual depending on the type of drug and drug
use method. Nasal, lung and chest problems are common addiction symptoms in
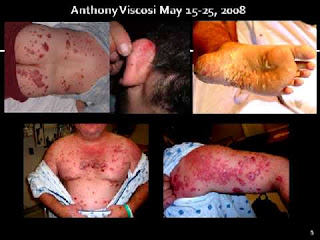
those who snort or smoke drugs like cocaine or marijuana. Skin
infections are common symptoms of drug addiction in those who inject drugs.
Because
drug addiction is both a physical and psychological issue, both physical and
psychological drug addiction symptoms can be seen (read about: physical and psychological effects of drug
addiction). Drug addiction symptoms include the following:
·
Unusual behavior
·
Change in responsiveness
·
Hallucinations
·
Changes to vital signs like heart rate, breathing and blood
pressure
·
Confusion, sleepiness, coma
·
Frequent blackouts
·
Abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea
·
Skin that is cool and sweaty or hot and dry
·
Infertility, sexual dysfunction
·
Heart, lung and other organ damage





























